Exploring the versatility of pharmaceutical lactose
Pharmaceutical‑grade lactose remains a highly versatile excipient in the drug and food industries. Lactose—a disaccharide naturally found in milk—is widely used in oral solid dosage forms because of its favourable properties such as solubility, physical stability, inertness, and compatibility with active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
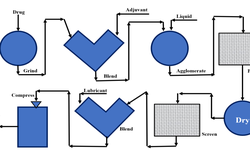
Different structural forms of lactose (for example α‑lactose monohydrate or anhydrous β‑lactose) and processing methods (milling, sieving, granulation, spray‑drying) are used to tailor its functionality for specific manufacturing routes—whether wet granulation, dry granulation, or direct compression. Factors like particle size distribution, density, and flowability are highlighted as critical quality attributes to ensure optimum performance in tablet and capsule production.
Lactose’s manufacturing chain is also discussed—from purification of whey or milk permeate to crystallization and drying—to ensure the required pharmaceutical purity and compliance with pharmacopoeial standards (e.g., USP, EP, JP). The article concludes that thanks to its functionality, safety profile, and wide range of available grades optimized for various dosage‑form technologies, lactose continues to be a preferred excipient for formulation scientists seeking reliable performance in oral solid dosage forms.

Comments
No comments posted yet.