Scientific papers
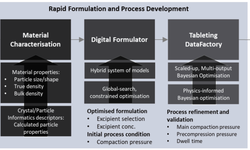
"Extended release formulations play a pivotal role in the pharmaceutical industry, contributing to the maintenance of steady plasma levels, reduction of side effects, and enhancement of therapeutic efficiency and patient compliance. Direct compression is a widely employed method for developing extended release formulations due to its inherent advantages, including simplicity, time savings, and cost-effectiveness. However, the successful formulation of extended release tablets through direct compression demands a thorough assessment and understanding of the attributes of the excipients involved.
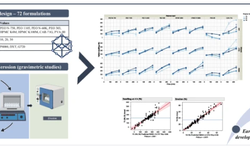
This study focuses on characterizing the compaction behavior of certain matrix-forming agents and diluents crucial for the development of extended release tablets. Fifteen commonly used excipients in extended release formulations were systematically evaluated for physical, compaction, and tablet properties. The assessment covered powder properties such as particle size, flow properties, and bulk density, which were intricately linked to the mechanical properties of the resulting tablets. A fully integrated approach was employed, and the data were subjected to analysis through principal component analysis (PCA).
The study revealed significant variability among the different excipients, showcasing the diverse characteristics influencing their performance. Importantly, the application of PCA proved to be a valuable tool for comparative analysis, pattern recognition, clustering, and establishing correlations between excipients and their properties. This approach facilitates the development and manufacturing of direct compressible extended release formulations by providing insights into the interrelationships among various excipients and their impact on tablet properties."

Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment