Advances in artificial intelligence in drug delivery and development
AI is transforming healthcare, particularly in drug delivery and development. This review explores AI's current and future roles in the pharmaceutical industry, focusing on smart drug delivery networks, sensors, drug repurposing, statistical modeling, and biotechnological simulations. It discusses AI's integration with nanotechnologies, advancements in drug discovery, and applications in drug formulation, clinical trials, and pharmacovigilance. The review addresses regulatory and ethical challenges, such as privacy, data security, and model interpretability. It emphasizes collaboration and knowledge sharing to overcome these challenges and enhance AI's impact on the pharmaceutical industry.
*Introduction:
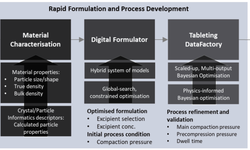
Drug delivery technology has evolved through three generations:
- First Generation: Improved solubility, stability, and bioavailability.
- Second Generation: Addressed biological barriers like cell membranes and the blood-brain barrier, focusing on targeted delivery and protection from degradation.
- Third Generation: Integrated solutions for physicochemical and biological challenges, optimizing drug properties and enhancing targeted delivery.
Recent research emphasizes improving water solubility, controlled delivery of complex drugs, and utilizing molecular biology, genomics, and monoclonal antibodies.
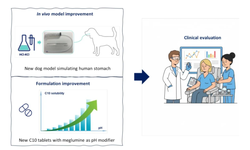
*Challenges in Drug Development:
- Target identification for nervous system disorders.
- Recapitulating diseases in animal models and addressing patient heterogeneity.
- Validating biomarkers and navigating regulatory processes.
- Overcoming batch-to-batch variation and ensuring economically viable drug design.
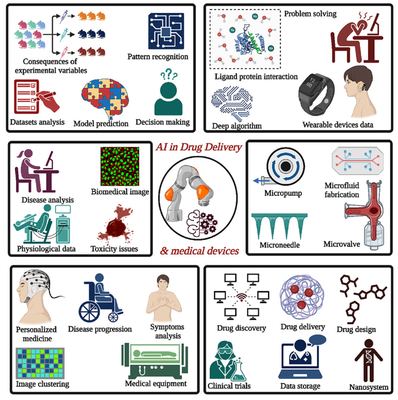
*AI and Machine Learning (ML) in Drug Development:
AI and ML improve various research areas, including target identification, disease understanding, drug candidate selection, protein structure prediction, and disease mechanism exploration. They also enhance biometric data analysis, precision medicine, and clinical trial data analysis.
*Limitations and Challenges of AI/ML:
- Potential biases in AI models.
- Need for large, diverse datasets.
- Interpretability and transparency of AI models.
- Ethical concerns regarding data ownership and patient consent.
*Integration and Collaboration:
Effective AI integration requires following evaluation processes, protocols, and regulatory guidelines. Collaboration and data sharing are crucial.
*Future Perspectives:
AI can transform the pharmaceutical industry, improving patient care and driving advancements in drug development and delivery. Addressing AI model limitations and ethical concerns will enhance its impact on global healthcare.
*Conclusion:
AI significantly contributes to drug development by enhancing efficiency and precision. Addressing challenges and ethical concerns will further advance AI's role in pharmaceuticals, leading to improved healthcare outcomes.
Comments
No comments posted yet.