Biopharmaceutical excipients: everything you need to know
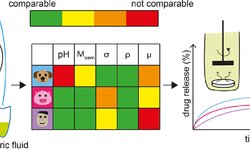
Biopharmaceutical excipients are specialized inactive ingredients used in biologic drug formulations — including monoclonal antibodies, vaccines, recombinant proteins, and gene therapies — to enhance stability, solubility, tonicity, and delivery performance. Although traditionally considered inert, these excipients play a key role in preserving fragile biologics during manufacturing and storage without altering their chemical activity. Their use extends beyond stabilization, as they can improve bioavailability, act as preservatives or antioxidants, and reduce operational costs while supporting targeted drug delivery. The industry is innovating new excipients to meet the demands of complex biologic therapies, including materials that assist with controlled release, poor solubility, and compatibility with challenging APIs. Despite challenges such as manufacturing complexity and raw material scarcity, growth in biopharmaceutical excipients is expected to continue, driven by increasing therapeutic applications and the need for advanced formulation solutions.

Comments
No comments posted yet.