Fluid bed and melt granulation in pharmaceutical manufacturing
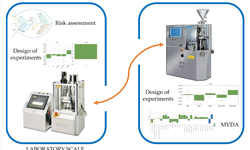
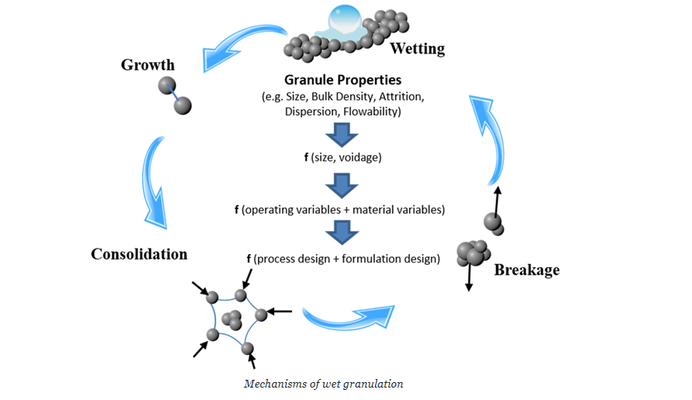
The article provides an in-depth look at granulation in pharmaceutical manufacturing, emphasizing fluid bed and melt granulation techniques. Granulation is essential for creating high-quality pharmaceuticals due to its benefits in density, flowability, and uniformity. The text outlines various granulation methods including dry granulation (using pressure), wet granulation (using a binder), and melt granulation (using a meltable binder).
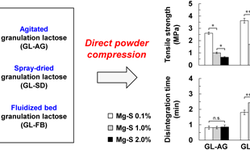
*Fluid bed granulation is highlighted for its superior reproducibility and process control. It involves suspending powdered material in high-velocity air, spraying a binder, and then drying the granules, which is efficient and scalable. Key advantages include precise control over particle size, reduced costs, and the combination of multiple processes in one instrument.
*Melt granulation combines a powdered API with a meltable binder, solidifying to form granules upon cooling. This method is efficient, scalable, and suitable for water-sensitive pharmaceuticals but not heat-sensitive drugs.
The text also describes the importance of controlling process parameters like air flow, temperature, and humidity to ensure desired granule properties. It discusses the stages of drying in fluid bed granulation, emphasizing the importance of managing residual moisture content.
Comments
No comments posted yet.