Formulating OSDs for poorly soluble drugs
Formulating oral solid dosage forms for poorly soluble drugs is increasingly challenging as many new APIs show low solubility and/or permeability. Effective development begins with understanding the API’s physicochemical profile (solubility, permeability, logP, pKa) and its BCS classification.
For BCS Class II molecules, formulators typically use solubility-enhancing strategies such as pH adjustment, surfactants, particle size reduction, salt selection, and solid dispersions produced via spray drying, hot-melt extrusion, or emerging technologies like KinetiSol.
More complex BCS Class III–IV drugs may require lipid-based systems, permeation enhancers, or other advanced approaches to improve absorption. Early-stage formulations can be simple (e.g., capsule filling), but later development often demands more robust techniques to ensure consistent bioavailability and scalability.
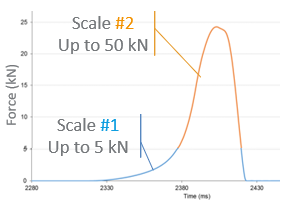
Throughout lifecycle development, tools like particle engineering and process analytical technology (PAT) help optimize manufacturing. Formulators must also consider regulatory constraints (e.g., nitrosamines) and patient-centric features to ensure safety, performance, and usability as drug molecules become more challenging.

Comments
No comments posted yet.