Retrospective analysis of the biopharmaceutics characteristics of solid oral Modified-Release drug products
This retrospective study, spanning from 2001 to 2021, examined submissions approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for Modified Release (MR) orally administered drugs [Extended-Release (ER) and Delayed-Release (DR)].
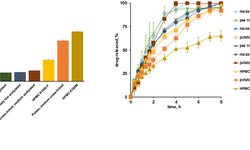
The analysis aimed to enhance understanding of the biopharmaceutics factors supporting ER and DR claims. Among 87 ER applications (23 capsules, 64 tablets) and 21 DR applications (10 capsules, 11 tablets), key findings include the prevalence of polymer matrix formulations in ER tablets and the use of hypromellose (HPMC). Most ER drug products demonstrated a reduction in dosing frequency and fluctuation compared to Immediate-Release (IR) references. DR formulations aimed at preventing degradation in the stomach and achieving localized release in the colon. ER and DR dissolution methods and dosing frequencies were largely aligned, with biphasic dissolution common in DR. Alcohol dose-dumping was infrequent in ER tablets and DR products but prevalent in ER capsules, mitigated by in vivo studies or warnings.
The study provides insights into the design, characteristics, and regulatory considerations for ER and DR drug products.

Comments
No comments posted yet.