Scientific papers
In this investigation, a co-processed excipient (Cop AA-MCC) was formulated through the combination of alginic acid (AA) and microcrystalline cellulose (MCC101) using a high-shear granulator on a laboratory scale. The resulting granules were compared with the primary materials (AA, MCC101), the dry mixture, and wet granulated MCC. The study delved into the impact of the ratio between the two components, the quantity of added water or binder during granulation, and the particle size on the properties of the prepared co-processed excipient.
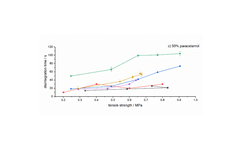
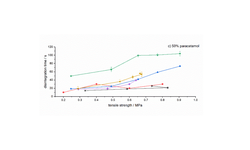
The findings indicated that optimal granule and tablet characteristics were achieved with a composition of 10% alginic acid, 90% MCC101, and 70% water. Furthermore, the co-processed product exhibited favorable tabletability, improved powder flowability, and notably faster disintegration time compared to the primary materials and a commercial co-processed excipient (Prosolv® ODT). Ultimately, the designed product demonstrated effective functionalities, positioning it as a valuable pharmaceutical excipient for industrial applications.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment