Scientific papers
Tablets continue to be the predominant oral dosage form, owing to their uncomplicated administration and relatively economical manufacturing. However, a significant drawback is the challenge of swallowing or chewing, particularly impacting special patient groups such as pediatric and geriatric patients. Orodispersible tablets (ODTs) present a solution to this issue by rapidly disintegrating in the mouth without the need for chewing or water intake. ODTs allow for the easy administration of liquid dosage forms while maintaining the high physical and chemical stability characteristic of solid drug dosage forms.
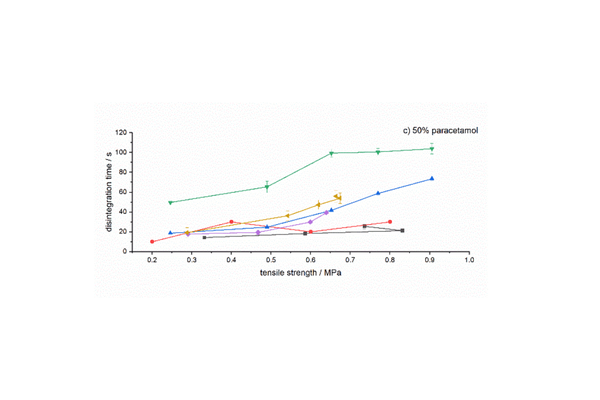
Our investigation centered on the direct compression of co-processed excipients (CPE) in conjunction with enalapril maleate, ibuprofen, and paracetamol as model APIs. The goal was to achieve multifunctional excipients through co-processing, striking a better balance between adequate strength and the necessary disintegration time. This study aimed to compare two newly developed co-processed excipients with those already commercially available. To achieve this, we analyzed the relationship between disintegration time and the attained tablet strength for seven CPEs, each incorporating one of the three APIs.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment