Scientific papers
Purpose: This study addresses the lack of reports on in vitro-in vivo correlation (IVIVC) model development for immediate-release (IR) formulations and the limited investigation of formulation and process impacts on spray-dried solid dispersions (SDD)-based tablets' pharmacokinetics (PK) in humans. The goal was to enhance the bioavailability of IR itraconazole SDD tablets and develop an FDA level A IVIVC to predict in vivo PK performance from in vitro dissolution testing.
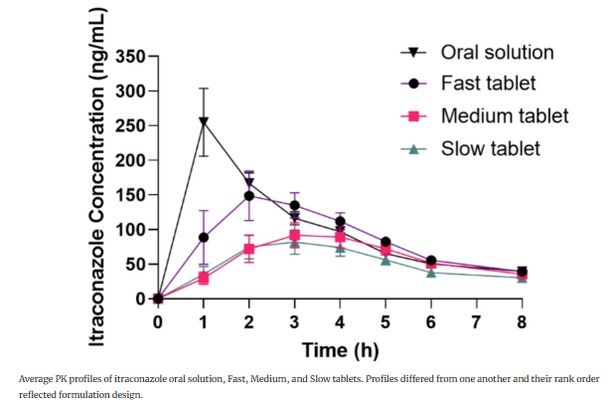
Methods: A differential-equation-based IVIVC model was used, involving an oral solution for post-dissolution disposition and Fast-, Medium-, and Slow-release tablets.
Results: The IVIVC met FDA level A requirements for internal predictability. In vitro dissolution used USP simulated intestinal fluid (phosphate buffer) at pH 6.4, with tablets triturated into particles to mimic in vivo disintegration differences. The model's credibility was assessed through verification and validation.
Conclusion: This study is the first to develop an FDA level A IVIVC for an amorphous solid dispersion, evaluating the impact of polymer grades, disintegrant levels, and dry granulation processing on SDD tablets' performance in humans.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment














