Scientific papers
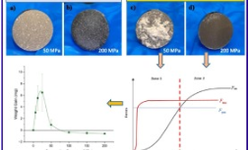
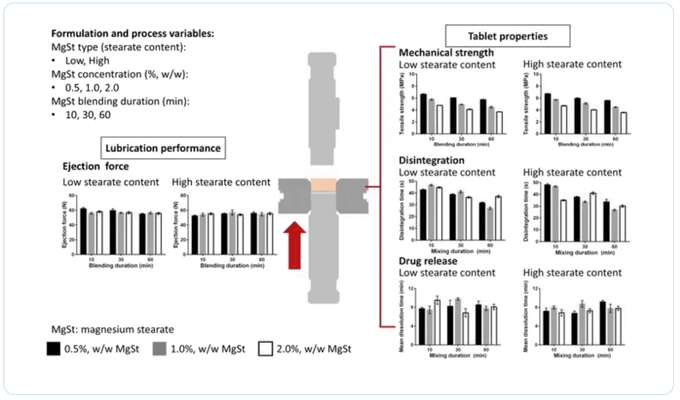
This research paper investigates the impact of different fatty acid compositions in magnesium stearate (MgSt), a common tablet lubricant, on tablet properties. The study focused on the significance of stearate and palmitate contents.
Key Findings:
MgSt with lower stearate content resulted in tablets with slightly higher tensile strength but longer disintegration time and slower drug release.
Lower stearate content led to poorer lubrication performance, resulting in a lesser reduction in tablet ejection force.
Longer blending time with MgSt generally reduced tensile strength, shortened disintegration time, and slowed drug release.
Higher MgSt concentration led to a greater reduction in tensile strength, longer disintegration time, and faster drug release.
Overall, the fatty acid composition of MgSt significantly influences tablet properties, particularly disintegration time and drug release. The study provides valuable insights for optimizing tablet formulations and improving product quality.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment