Scientific papers
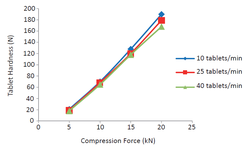
Orodispersible tablets, also known as orally disintegrating tablets (ODTs), are pharmaceutical dosage forms designed to enhance the in vivo oral disintegration and dissolution rates of a pharmaceutical product. To achieve rapid disintegration rates, the tablet formulation must exhibit high porosity, low density, and low hardness.
Various preparation methods are commonly employed to manufacture ODTs, including molding, lyophilization, freeze-drying, and direct compression. The fundamental approach in developing ODTs through direct compression involves blending a filler, superdisintegrant, lubricant, and an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), followed by compressing the mixture.
Mannitol is frequently utilized as a diluent or bulk excipient in ODT formulations. Roquette has introduced a new generation of coprocessed mannitol-based excipients for ODT formulation, such as PEARLITOL® Flash, which combines mannitol and starch. Both mannitol and starch comply with international pharmacopoeias, and the synergistic composition is specifically engineered for rapid disintegration, ensuring a smooth texture without the need for additional superdisintegrants.

Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment