Active tablet coating with amorphous solid dispersion of ibuprofen–HPMCAS from organic solution
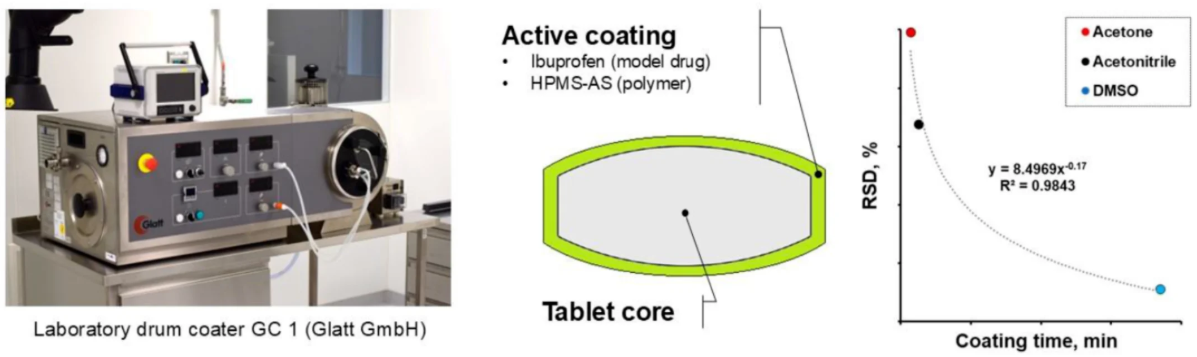
This study explores an active coating approach for tablets in which a poorly soluble drug (ibuprofen) is incorporated as an amorphous solid dispersion on the surface of a tablet core using standard pan-coating equipment. Tablet coating is traditionally used to improve appearance, swallowability, or release profile, but applying a drug-loaded amorphous coating is less common due to challenges like limited surface area and control of coating uniformity. The researchers investigated coatings made from solutions of ibuprofen and HPMCAS in different organic solvents to understand how solvent choice affects coating process, drug dosing accuracy, and uniformity. They found that using solvents with different boiling points affects coating time, solvent retention, and dosage precision. Overall, the work demonstrates that drug-containing coatings can achieve reliable dosage uniformity on tablets, offering a potential strategy for delivering poorly soluble APIs via active surface coatings and improving oral bioavailability.
Comments
No comments posted yet.