Concerns regarding calcium carbonate as an alternative excipient for titanium dioxide
The article titled discusses the potential use of calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) as a replacement for titanium dioxide (TiO₂) in pharmaceutical applications, particularly in film coatings and capsule shells. TiO₂ has been widely used for its white color and opacity, enhancing the aesthetic appearance and stability of drug products. However, due to safety concerns, including potential genotoxicity, the European Commission banned the use of TiO₂ as a food additive in 2022, and there is a possibility that this ban may extend to pharmaceutical products.
Calcium carbonate is being considered as an alternative because it is the only other white colorant approved for use in pharmaceuticals within the European Union. It is already utilized in the nutraceutical and dietary supplement industries. However, the article highlights several concerns regarding its suitability as a replacement for TiO₂:
- Opacity and Coverage: Calcium carbonate may require higher concentrations to achieve the same level of opacity as TiO₂, potentially leading to less effective protection for light-sensitive drugs.
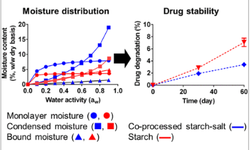
- Drug Stability: As a basic compound, calcium carbonate can alter the local pH of the dosage form, which may affect the stability of certain active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). It can also form complexes with specific drugs, potentially impacting their efficacy
- Compatibility Studies: Given these potential interactions, the article recommends conducting compatibility and bioavailability studies when replacing TiO₂ with calcium carbonate to ensure the stability and effectiveness of the pharmaceutical product
In conclusion, while calcium carbonate presents a viable alternative to TiO₂ in pharmaceutical formulations, careful consideration and testing are necessary to address the associated challenges and ensure product quality.

Comments
No comments posted yet.