Scientific papers
Mannitol possesses physical and chemical inertness, along with several advantageous organoleptic properties, making it the preferred excipient for formulating nutraceutical tablets. The [starch + mannitol] compound PEARLITOL® Flash serves as a ready-to-use directly compressible platform, facilitating the production of orally dispersible tablets.
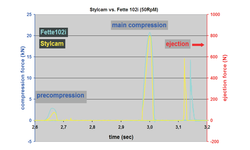
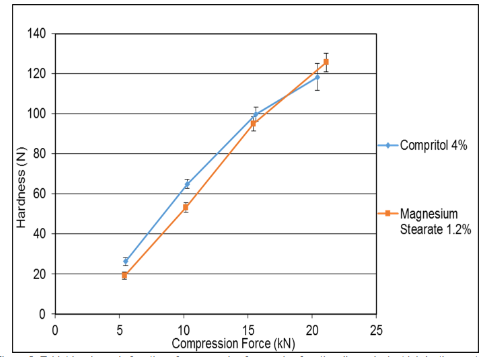
However, it is known that mannitol exhibits a high lubrication requirement to achieve moderate ejection forces and prevent potential tableting issues such as stickiness and lamination [3]. Existing literature suggests the use of > 1% Magnesium Stearate (Mg stearate) for optimal tableting of pure mannitol. Mg stearate plays a crucial role in various aspects of the compaction process of pharmaceutical powders. Its primary function is to prevent interactions between the compressed powder and the surfaces of the die walls and punches, which could lead to gripping, sticking, and tablet etching. Additionally, it interferes with the inter-particulate interactions of the compressed powder, influencing the rearrangement of individual particles and cohesive properties post-compaction.
The impact of Mg stearate lubricant during powder compaction is more pronounced on plastic materials like microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) [1], as opposed to fragmentary materials such as lactose, textured mannitol [3], and dicalcium phosphate [2].
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment