Scientific papers
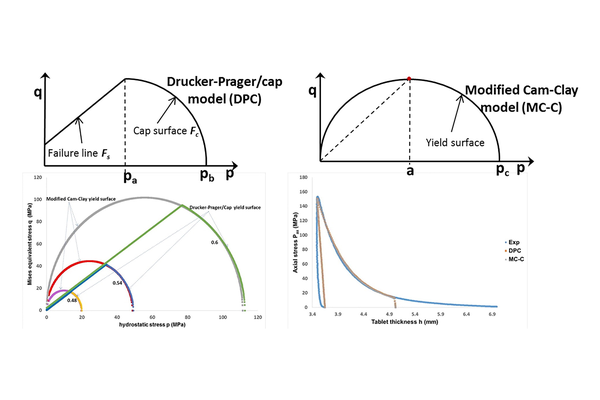
Numerical simulation using the finite element method is a common approach for modeling die compaction processes. In the pharmaceutical field, the widely used Drucker-Prager/Cap (DPC) model is employed to study powder mechanical behavior. This study introduces the modified Cam-Clay (MC-C) model, another classical but less commonly used model. The main advantage of the MC-C model lies in the ease of determining its parameters compared to the DPC model. The yield surface of the MC-C model takes the form of an elliptical curve. The study compares the MC-C model to the DPC model to evaluate its capability in describing powder behavior during compression. Experimental tests were conducted to characterize the parameters of both models, followed by simulations. The overall powder compression behavior was assessed using model equations and compression curve plots. Spatial distributions of relative density and axial stress were analyzed to compare local compact behavior, including stress concentration and areas of low/high density. The results from both models were nearly identical for flat-faced punches and concave-face punches. This suggests that the MC-C model effectively describes the die compaction of pharmaceutical powder.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment