Scientific papers
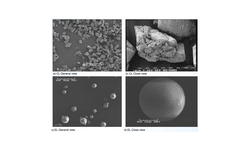
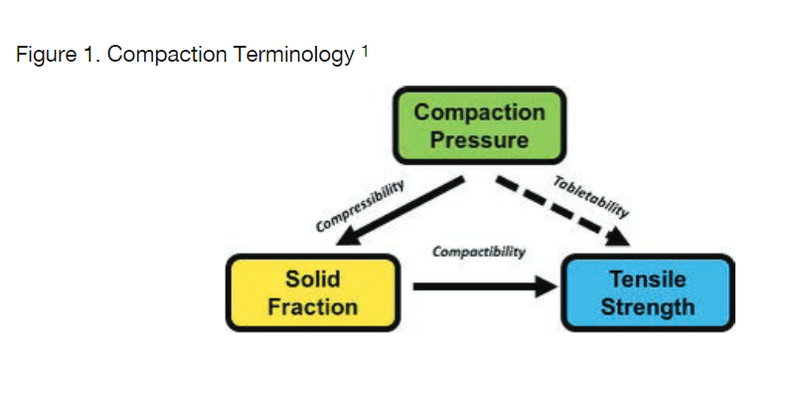
Starch-based excipients are commonly employed in the creation of solid oral formulations due to their properties as binders, fillers, or disintegrants. Maize starches, chosen for their inert and stable nature with low water activity, stand out as the preferred option for managing moisture in solid oral dosage forms. These excipients, derived naturally, are readily available and well comprehended by both formulators and regulators. While unmodified starch (native starch) is recognized for its inadequate flow and compressibility, making it unsuitable as a primary filler for direct compression, this study aims to assess the compressibility and flow of a newly introduced directly compressible starch (StarTab®) through compaction simulation and rotary tablet press testing.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment