Scientific papers
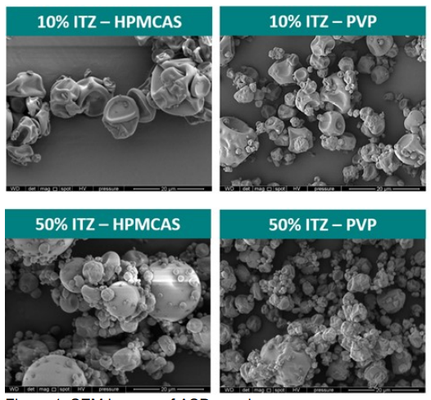
Amorphous solid dispersions (ASD) are commonly employed to enhance the solubility and bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs. Immediate-release tablets are often chosen as the final dosage form for ASDs. Therefore, the careful selection of excipient polymers and drug loading is crucial for both the manufacturability and bioavailability of ASD tablets. In this project, ASDs were crafted using the spray drying technique, and ASD tablets were formulated using a compaction simulator. The project investigated the impact of polymer types and drug-polymer ratios on bulk powder properties, compaction behavior, and the physical stability of ASDs. Itraconazole (ITZ) served as the model drug, and two polymers, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose acetate succinate (HPMCAS) and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), were employed in the study.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment















