Scientific papers
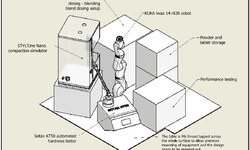
With the growing interest in chronopharmaceutics, press-coated tablets have emerged as a pivotal technology in the realm of modified release drug delivery systems. While considerable research has explored their advantages in terms of drug release, a comprehensive understanding of the compaction process for press-coated tablets is still evolving. In particular, the impact of geometric parameters, such as the ratios between the thickness/diameter of the core and the thickness/diameter of the entire tablet, has not been extensively explored. Additionally, there is a limited body of literature on how press-coating compression affects the final structure and properties of the core.
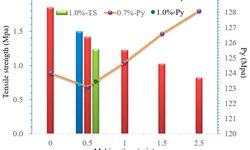
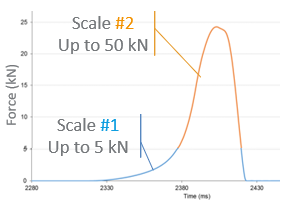
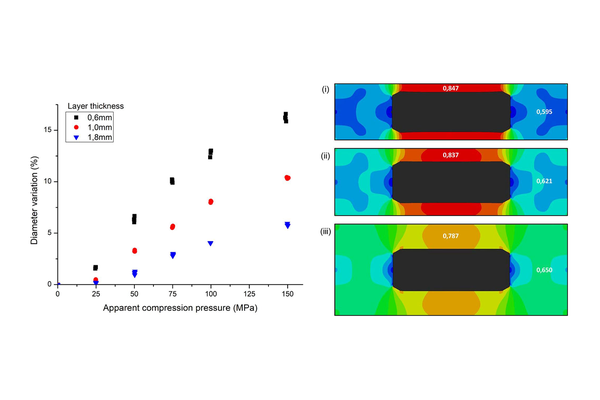
This study, comprising both experimental and numerical approaches, seeks to address these aspects. The investigation unveiled substantial stress concentrations on the core during compression, leading to significant permanent deformations, especially when the ratio between the core thickness and the total tablet thickness was high. The mechanical properties of the core tablet were also observed to be influenced, with density and strength initially decreasing before rebounding during the coating compression. This phenomenon was found to be contingent on the triaxiality of the stress state, determined by the ratio between stresses in different directions, itself reliant on the two studied geometrical parameters. Given that the properties of the core impact release attributes, the dimensions' ratios between the core and the entire tablet (thickness, diameter) should be regarded as critical parameters in the manufacturing of press-coated tablets.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment