Scientific papers
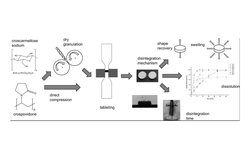
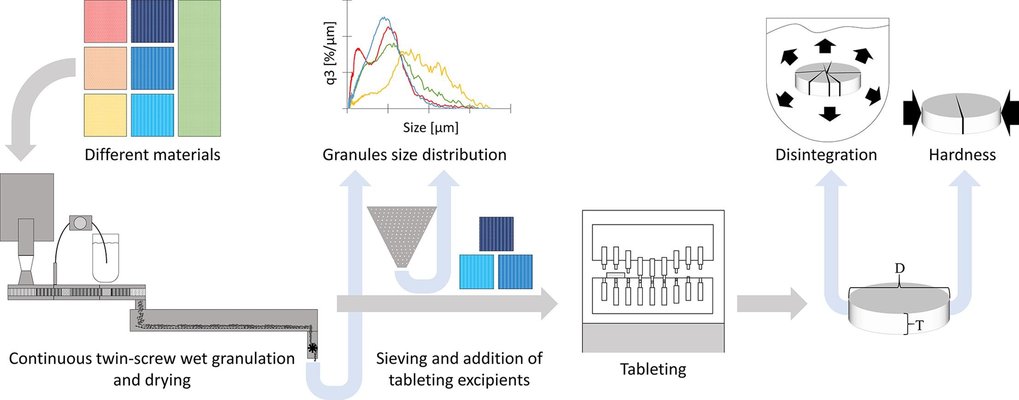
The study explored the effects of the localization (intragranular, split, or extragranular) of three superdisintegrants (croscarmellose sodium, crospovidone, sodium starch glycolate) on granules and tablets produced through twin-screw granulation. The goal was to determine the most suitable disintegrant type and localization for lactose tablets formulated with various hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) types. The disintegrants were observed to decrease particle size during granulation, with sodium starch glycolate having the least impact. Tablet tensile strength remained largely unaffected by disintegrant type or localization. On the other hand, disintegration was influenced by both disintegrant type and localization, with sodium starch glycolate showing comparatively lower effectiveness. Intragranular croscarmellose sodium and extragranular crospovidone were identified as favorable under specific conditions, providing satisfactory tensile strength coupled with rapid disintegration. These conclusions were drawn for one HPC type, and the appropriateness of the best disintegrant-localization combinations was validated for two additional HPC types.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment