Scientific papers
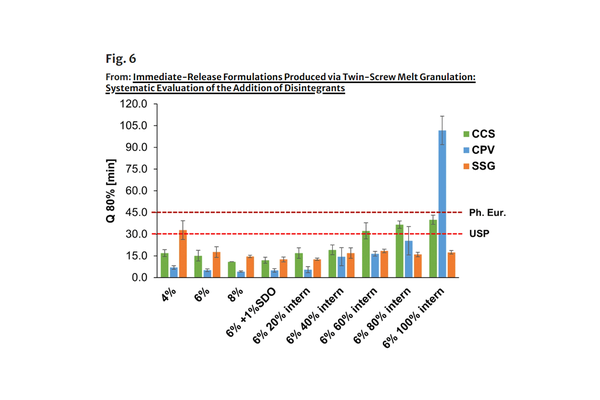
The present study investigated the impact of the location and quantity of various superdisintegrants on the characteristics of tablets produced through twin-screw melt granulation (TSMG). Sodium-croscarmellose (CCS), crospovidone (CPV), and sodium starch glycolate (SSG) were incorporated in different proportions both intra- and extra-granularly. Tabletability, compactibility, compressibility, as well as friability, disintegration, and dissolution performance, were evaluated. Extra-granular addition led to the fastest disintegration and dissolution, with CPV outperforming CCS and SSG. Despite a lower solid fraction (SF) for CPV granules, only a minor reduction in tabletability was observed, attributed to the high plastic deformation of the melt granules.
Intra-granular addition of CPV resulted in a prolonged dissolution profile, linked to a porosity loss during tableting. A 100% intra-granular addition of CPV significantly decreased disintegration efficiency, while SSG performance remained unaffected by the granulation process. CCS, when added in the total proportion during the granulation phase, was not suitable for immediate-release formulations, though its efficiency was less impaired compared to CPV. The shortest disintegration (78 s) and dissolution time (Q80: 4.2 min) were achieved with extra-granular CPV. Intra-granular CPV and CCS led to increased disintegration time and Q80. However, only SSG exhibited a location and process-independent disintegration and dissolution performance at higher levels of approximately 500 s and 15 min, respectively.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment