Scientific papers
Film coatings on tablets are commonly used to confer specific properties, such as achieving particular drug release profiles. The surface characteristics of tablet cores play a crucial role in the coating process, directly impacting the application of the coating dispersion and, consequently, the quality attributes of the film. The objective of this study was to explore the influence of various functional excipients in tablet cores on the apparent adhesion of film coatings.
Commonly utilized lubricants (magnesium stearate and sodium stearyl fumarate) and disintegrants (croscarmellose sodium, crospovidone, and sodium starch glycolate) were combined with microcrystalline cellulose and compressed into tablet cores. Additionally, a commercially available co-processed excipient for direct compression was included in the study. A hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC)-based tablet coating was then applied to the tablet cores in a drum coater, and the adhesion of the coating was assessed.
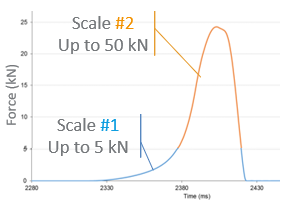
In general, the tensile strength of the tablet cores emerged as the dominant factor influencing apparent film coating adhesion. However, the incorporation of functional excipients in the tablet cores led to a reduction in the adhesion of film coatings compared to pure microcrystalline cellulose. Lubricants had a more adverse effect than disintegrants on adhesion. Ultimately, the measured film coating adhesion was determined to result from fundamental adhesion between the film coating and the tablet surface and cohesive failure within the tablet core.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment