Scientific papers
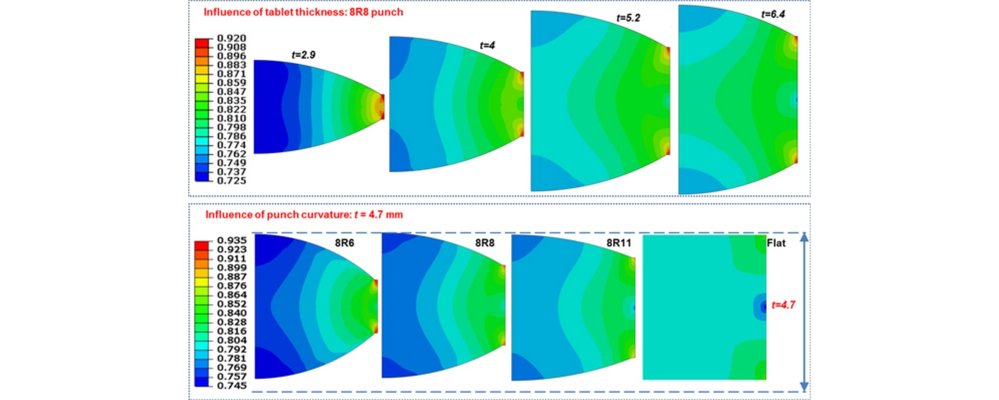
The finite element method was utilized to examine the impact of tablet thickness and punch curvature on the density distribution within convex-faced (CF) tablets. The modeling was conducted on two pharmaceutical excipients (anhydrous calcium phosphate and microcrystalline cellulose) using the Drucker–Prager Cap model in Abaqus® software, with parameters derived from experimental tests. Various punch shapes based on industrial standards were employed, including a flat-faced (FF) punch and three convex-faced (CF) punches (8R11, 8R8, and 8R6) with an 8mm diameter. The study explored different tablet thicknesses under a constant compression force. Simulations of the compaction process for CF tablets with increasing thicknesses revealed a significant alteration in the density distribution within the tablet. For smaller thicknesses, low-density zones were concentrated towards the center. The density inside CF tablets exhibited non-uniformity, with low-density regions at the center of the two faces, while the distribution within FF tablets remained nearly independent of tablet thickness. These findings indicated that FF and CF tablets, even produced under the same compression force, exhibit distinct density patterns at the center of the compact. Consequently, variations in tensile strength, as measured by diametral compression, are anticipated, and this was confirmed by experimental tests.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment













