Scientific papers
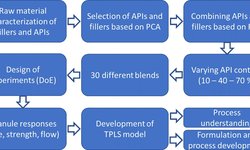
This study aimed to explore the responsiveness of various drug formulations to differences in process parameters based on previously established scale-up strategies. Three distinct formulations were employed for scale-up experiments, transitioning from a QbCon® 1 with a 16 mm screw diameter and a 2 kg/h throughput to a QbCon® 25 line featuring a 25 mm screw diameter and a 25 kg/h throughput. Two of these formulations shared a similar composition of excipients but varied in the API added to the blend, investigating the impact of the API's solubility during twin-screw wet granulation. The third formulation, designed for controlled release, incorporated different excipients and a substantial fraction of HPMC.
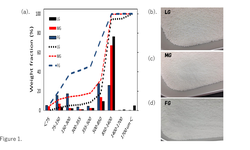
The L/S-ratio had to be tailored for each formulation, considering that the blends exhibited significant variations in their response to water addition and overall granulation behavior, dependent on the binder and overall composition. Pre-milling, considerable differences in granule size distributions based on scale were observed for all formulations, with Earth Mover’s Distance ranging from 140 to 1100 µm (higher values indicating lower similarity).
However, post-milling, no substantial differences in granule properties (e.g., Earth Mover’s Distance for GSDs: 23-88 µm) or tablet tensile strength (consistently > 1.8 MPa at a compaction pressure of 200 MPa for all formulations, with a coefficient of variation < 0.1, indicating high robustness) were noted. This successful scale-up was achieved irrespective of the selected formulations.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment