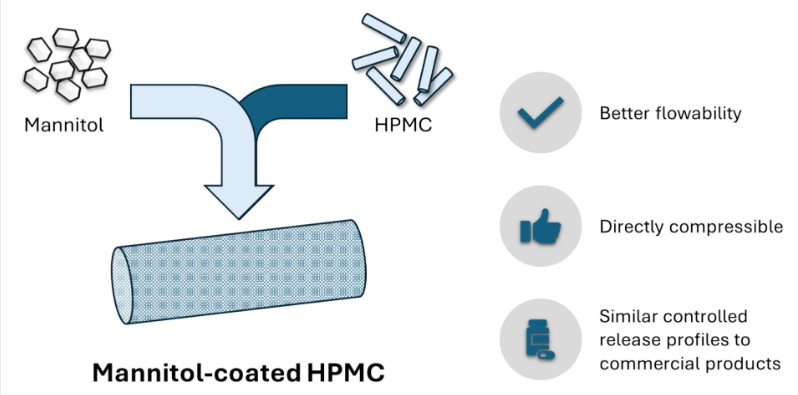
Mannitol-coated hydroxypropyl methylcellulose as an alternative directly compressible controlled release excipient
One of the most common forms of controlled release technology for oral drug delivery involves dispersing an active ingredient in a hydrophilic matrix-forming polymer like hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC), which is then tableted via direct compression. However, HPMC can present issues during direct compression due to its poor flowability. To address this, mannitol syrup was spray-coated over fluidized HPMC particles to create co-processed HPMC–mannitol at ratios of 20:80, 50:50, and 70:30. Pure HPMC particles, co-processed HPMC–mannitol, and their respective physical mixtures were evaluated for powder flowability, compression profiles, and controlled release performance.
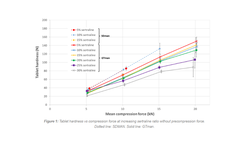
The co-processed HPMC–mannitol particles demonstrated improved flowability compared to pure HPMC particles. Strong tablets exceeding 2 MPa could be produced at moderate to high compression forces of 150–200 MPa. The dissolution profile could be adjusted to achieve desired release rates by altering the HPMC–mannitol ratios. Co-processed HPMC–mannitol offers a valuable option for formulators designing controlled release formulations for direct compression.
Materials
Direct compression grade HPMC (HPMC DC; METHOCEL™ DC2 K4M, HPMC 2208, 4000 mPa.s grade, Colorcon, USA) and co-processed HPMC–mannitol (mannitol CR-H, PEARLITOL® CR-H, Roquette, France) were used as received. Various ratios of HPMC–mannitol co-processed samples (HPMC:mannitol 70:30, 50:50, and 20:80, corresponding to H70M30–CP, H50M50–CP, and H20M80–CP, respectively) were manufactured by Roquette, France, where mannitol syrup was sprayed onto fluidized HPMC particles (Benecel™ K4M CR, Ashland).
Comments
No comments posted yet.