MEGGLE highlights role of excipient properties in alcohol-induced dose dumping AIDD
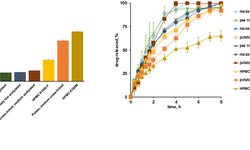
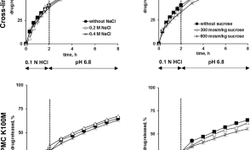
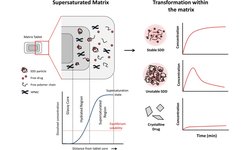
The white paper from MEGGLE emphasizes the significance of excipients in addressing alcohol-induced dose dumping (AIDD) in modified-release tablet formulations. AIDD occurs when drugs prematurely release into the bloodstream due to alcohol ingestion, potentially leading to overdosing. The paper discusses the scientific factors contributing to AIDD, various regulatory approaches, and mitigation strategies. It highlights the importance of excipient properties such as wettability, solubility, and swellability in resisting AIDD, and introduces a co-processed excipient called RetaLac® designed to create an alcohol-resistant matrix system. The authors stress the need for regulatory harmonization in testing regimes to address AIDD effectively.

Comments
No comments posted yet.