Trends in amorphous solid dispersion drug products approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration between 2012 and 2023
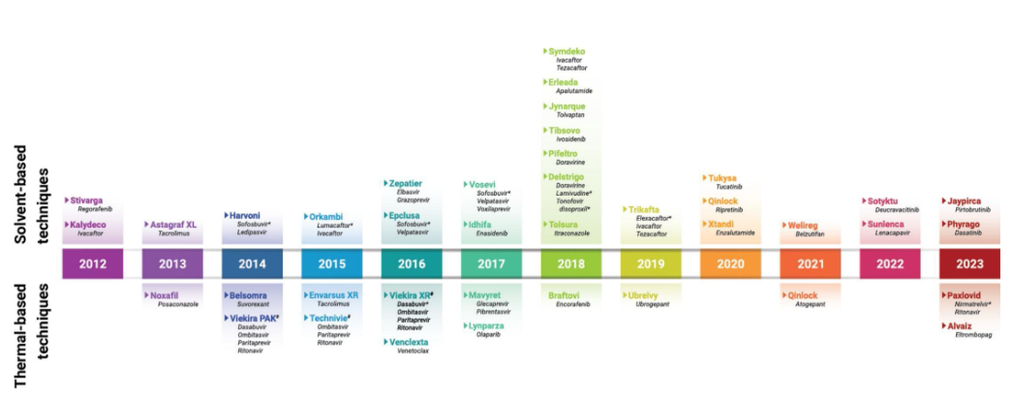
Between 2012 and 2023, the U.S. FDA approved 48 drug products (DPs) containing amorphous solid dispersions (ASDs), involving 36 unique amorphous drugs across 10 therapeutic categories, predominantly antiviral and antineoplastic agents. Common ASD polymers include copovidone (49%) and hypromellose acetate succinate (30%), with spray drying (54%) and hot melt extrusion (35%) being the primary manufacturing methods. Tablet forms are most prevalent, with capsules also common. Some DPs offer flexible dosing options for pediatric and other populations.
Key trends and findings include:
- Excipients: Diluents like MCC (66.7%) and lactose (41.7%) are widely used, with combinations optimizing tablet properties. Disintegrants, mainly croscarmellose sodium, are present in most DPs. Lubricants like magnesium stearate (70.8%) are common, aiding in manufacturing.
- Film Coating: 79.1% of DPs have film coatings, with HPMC and PVA being the most common types, offering benefits like moisture barrier properties.
The article emphasizes the variety of formulation components and manufacturing techniques used to optimize the performance and stability of ASD drug products. Download or read the full article for detailed insights.
Comments
No comments posted yet.














