Scientific papers
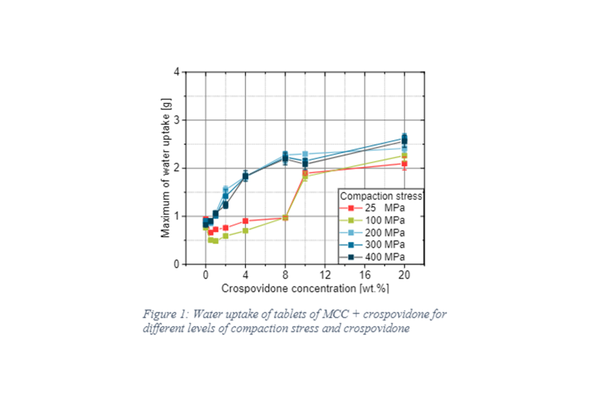
Tablets represent the predominant dosage form in the pharmaceutical industry, ensuring rapid drug release through quick tablet disintegration facilitated by the absorption of water into the tablet. As a result, the uptake of water and subsequent volume expansion are crucial prerequisites for tablet disintegration. This study involved compacting binary mixtures of excipients into tablets with varied structural and mechanical properties to assess the impact of formulation and process parameters on water uptake and the resultant swelling force of the tablets. The findings highlighted significant effects of disintegrant concentration and tablet porosity on both the absorbed amount of water and the exerted swelling force. The results underscored the utility of water uptake and swelling force measurements as valuable tools for enhancing our comprehension of tablet disintegration.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment