Scientific papers
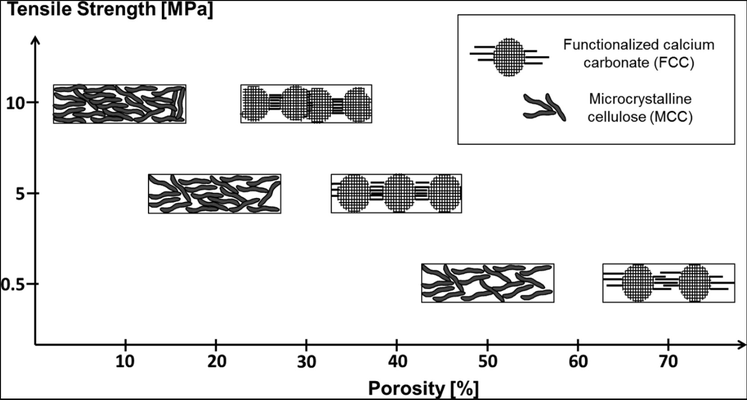
In this study, our objective was to characterize the compressibility and compactibility of a novel pharmaceutical excipient known as functionalized calcium carbonate (FCC). We investigated three different modifications of FCC and compared the compressibility and compactibility values with those of mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), and ground calcium carbonate (CC 330). Additionally, we analyzed mixtures containing paracetamol with either MCC or FCC at various drug load percentages (0%, 25%, 50%, 75%, and 100% w/w). The compaction and compression behavior of the mixtures were assessed using Heckel analysis, modified Heckel analysis, and Leuenberger analysis. The compaction analysis of FCC revealed distinct properties, such as plastic deformability, distinguishing it from ground calcium carbonate and resembling those of MCC. This behavior was attributed to the highly lamellar structure of FCC particles, with thickness comparable to that of a single crystal unit cell. Based on Leuenberger parameters, we concluded that tablet formulations with FCC exhibited mechanical properties equal to or superior to those formulated with MCC. FCC tablets with high tensile strength were achieved at low compressive pressures, highlighting the promising suitability of FCC for the preparation of solid dosage forms.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment