Scientific papers
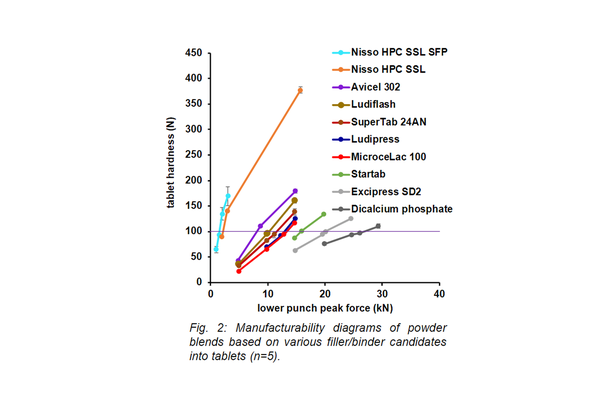
Probiotics show potential as therapeutic options for bowel disorders and diseases. However, these intestinal bacteria are highly susceptible to oxidative degeneration, a process exacerbated by the elevated compression forces typically employed in tablet preparation. Excipients, commonly referred to as fillers with binding capacities, present an opportunity to work at reduced compaction forces, achieving adequate tablet hardness, low porosity, favorable disintegration behavior, and the preservation of viable probiotic cells. The filler/binder materials investigated in this study exhibit diverse chemical compositions and can be co-processed excipients, with a prerequisite for excellent flowability.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment