Scientific papers
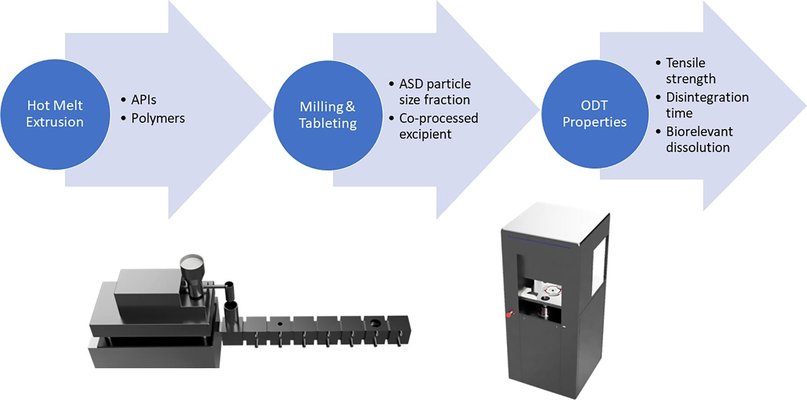
The development of patient-friendly oral solid dosage forms for amorphous solid dispersions (ASDs) remains a challenging task. Orodispersible tablets (ODTs) present a promising alternative to enhance patient compliance. Two distinct ASDs were created through hot melt extrusion (HME), employing PVPVA as the polymer for ritonavir (RTV) and HPMCAS for lopinavir (LPV). The extrudates underwent milling, sieving, and blending with established co-processed excipients (CPE), Hisorad® (HRD), or Ludiflash® (LF), before the tableting process. Interestingly, the selected ASD particle size emerged as a crucial parameter for achieving rapid disintegration and high mechanical strength. For PVPVA-based ASDs, larger particle sizes (>500 µm) facilitated swift disintegration, even within 30 seconds for ODTs loaded with 50% ASD. Conversely, smaller particles resulted in significantly longer disintegration times. The choice of CPE played a substantial role for PVPVA-based ASDs, with only Hisorad® leading to well-performing ODTs. In contrast, for HPMCAS-based ASDs, smaller particle sizes (180–500 µm) proved beneficial in overcoming the poor compressibility of the ASD matrix polymer. ODTs containing LPV could be successfully produced using both CPEs, even with higher ASD loads of up to 75%, while maintaining remarkably fast disintegration times.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment