Scientific papers
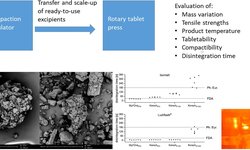
Objective: This study aims to assess the performance of various superdisintegrants (SD) in the production of orodispersible mini tablets (ODMT) through direct compression.
Methods: Twenty-three formulations, varying in SD type, concentration, and lubricant, were utilized to manufacture ODMT. Subsequently, the ODMT were characterized for friability, porosity, tensile strength, in vivo, and in vitro disintegration time (DT).
Results: The findings indicate that the presence, type, and concentration of SD did not impact friability, porosity, or tablet tensile strength. Concerning in vivo DT, only cross-linked poly (vinyl pyrrolidone) exhibited improved DT across all tested formulations. Additionally, results revealed that when utilizing microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) exceeding 20% in the formulation, DT was prolonged. Cross-linked carboxymethyl cellulose accelerated DT when MCC content was below 20%. However, cross-linked carboxymethyl starch and calcium alginate showed no improvement in DT. In vitro DT results were consistently shorter than in vivo outcomes, and there was no correlation with the in vivo assessment.
Conclusions: This study underscores the necessity to develop improved in vitro testing methods that closely mimic in vivo conditions and are tailored to ODMT. Standardizing test methods for ODMTs should be accompanied by an enhanced understanding of SD mechanisms.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment