Scientific papers
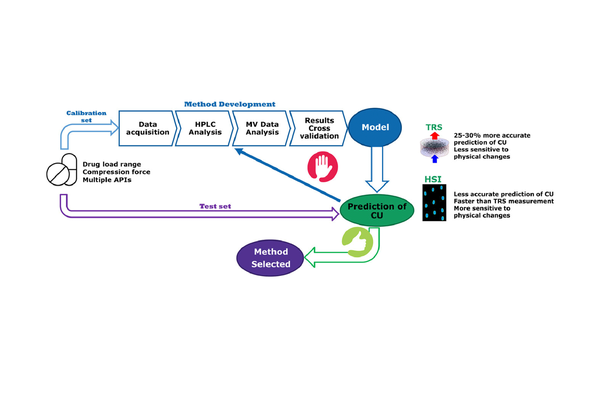
Objective: The present study aimed to investigate and compare the efficacy of fast and non-destructive Transmission Raman Spectroscopy (TRS) and Near Infrared Hyperspectral imaging (NIR HSI) in developing predictive quantitative methods for assessing the content uniformity (CU) of tablets.
Methods: Two sets of tablets were prepared, one comprising single Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API) with caffeine concentrations ranging from 12.75%w/w to 17.75%w/w, and another consisting of double API tablets with model API A* (5.25%w/w - 9.25%w/w) and caffeine (7%w/w – 13%w/w) at five concentration levels. Chemometric prediction models were created using partial least square (PLS 1) and subsequently tested on a separate set of tablets for both single and double APIs.
Results: Calibration PLS1 models were established for single and double APIs using a combination of S-G 1st derivative and SNV data pre-processing steps, providing optimal model performance with the lowest cross-validation error and bias. The root mean square error of prediction (RMSEP) for the PLS1 model in single API caffeine tablets was 0.27% for TRS and 0.36% for NIR HSI. The PLS1 models built using TRS for double API tablets showed an RMSEP of 0.29% for API A and 0.34% for caffeine. Similarly, for NIR HSI prediction models, the RMSEP was 0.43% for API A and 0.56% for caffeine.
Conclusion: Overall, TRS demonstrated a 25–30% more accurate prediction capability compared to NIR HSI in this specific sample set. Nevertheless, both TRS and NIR HSI exhibit the potential to serve as rapid, nondestructive techniques for replacing classical wet-chemistry methods in the at- or off-line determination of tablet CU.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment