Scientific papers
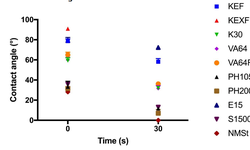
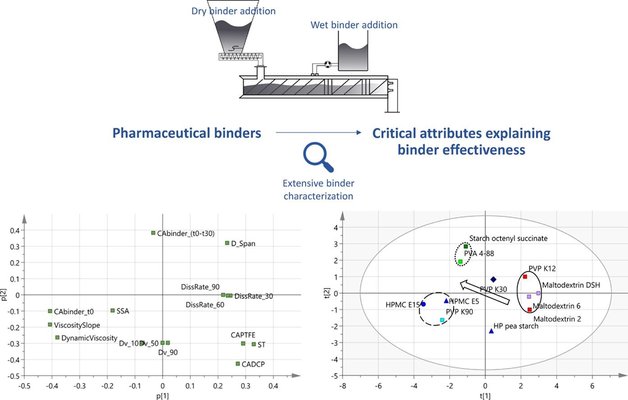
The impact of various binders on the quality of granules produced through continuous twin-screw wet granulation was investigated. Anhydrous dicalcium phosphate served as a poorly soluble filler, and binders were added either in a dry or wet manner. Additionally, both dry and wet binder characteristics were assessed, and their relationship to binder effectiveness was established. PVA 4–88 and starch octenyl succinate demonstrated the lowest granule friability at low liquid-to-solid ratios, indicating the highest binder effectiveness. This was attributed to rapid binder activation facilitated by the fast wetting kinetics of the binder, efficient wetting of DCP particles, and effective spreading in the powder bed. Consequently, early-stage wettability measurements were deemed highly important in formulation development. Moreover, the study highlighted that increased stickiness of the binder surface, influenced by high binder viscosity and slow dissolution kinetics, also positively impacted binder effectiveness. In conclusion, the research identified critical binder attributes that significantly influence the granulation process of dicalcium phosphate. Additionally, the study successfully demonstrated the efficacy of dry binder addition in creating high-quality granules.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment