Scientific papers
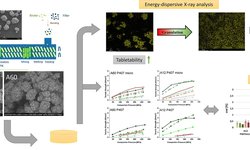
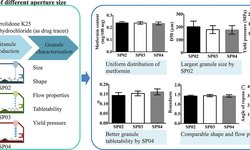
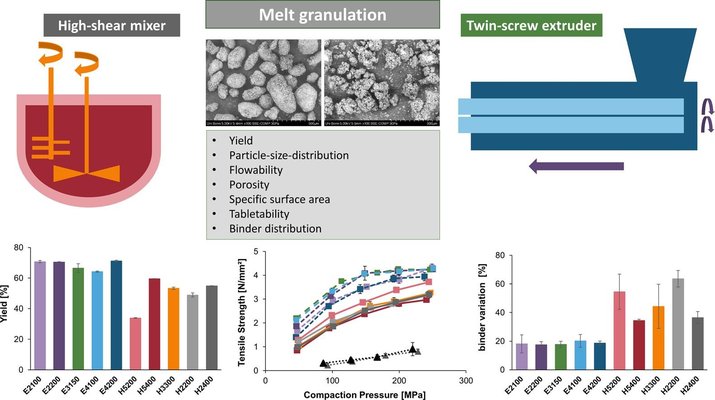
Melt granules containing DI-CAFOS® A12 and 15% (w/w) Kolliphor® P407 were produced using a twin-screw granulator (TSG) under five different conditions (varied screw speed and throughput). These were then compared with granules manufactured in a high-shear granulator (HSG), where variations included the rotation speed of the chopper/impeller and granulation time. The evaluated characteristics of the granules included process yield, particle-size distribution (PSD), particle morphology, flowability, porosity, specific surface area (SSA), tabletability, compressibility, and binder distribution.
In comparison to TSG, HSG-produced granules exhibited a more spherical shape, lower porosity, smaller mean particle size, and superior flowability. Conversely, TSG granules displayed a more elongated structure, higher porosity, larger mean particle size, and a smaller SSA. Regarding the compression process, tablets made from TSG granules showed higher tabletability compared to HSG granules, while compressibility remained similar.
For TSG granules, energy-dispersive-X-ray (EDX) measurements on the tablet surface indicated an enhanced and homogeneous binder distribution. Furthermore, EDX analyses revealed that more binder was present between individual particles, resulting in stronger bonding.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment