Scientific papers
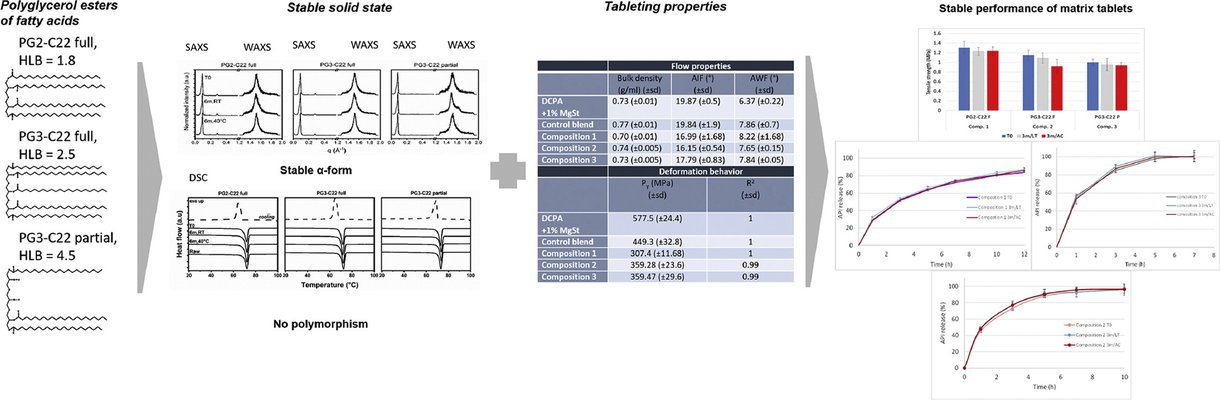
This study introduces an innovative approach to developing stable extended-release matrix tablets through direct compaction. The chosen molecules belong to polyglycerol esters of fatty acids (PGFAs), a category of lipid-based excipients (LBE) known for their advanced solid-state stability. The development of extended-release tablets employed three PGFA compounds with a Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balance (HLB) range of 1.8 to 4.5, serving as matrix-forming agents. The model substance chosen was Metformin HCl, a freely water-soluble Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API).
The deformation behavior and flow properties of tableting blends were examined, comparing those with and without PGFAs. Blends containing PGFAs exhibited reduced yield pressure and diminished internal friction between particles, indicating the potential for plastic behavior of PGFAs and improved flow properties of their blends. These lipid-API-filler blends were directly processable via direct compression without any prerequisite treatments like granulation. The resulting tablets displayed the desired tensile strength and friability.
The application of PGFAs with varying HLB values allowed for the customization of the API release profile for different time periods while maintaining the same lipid concentration in the tablet. The stability of the release profile was attributed to the stable solid-state nature of lipids as matrix agents. Importantly, no in vitro cytotoxic effects were observed when assessing dehydrogenase activity.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment