Scientific papers
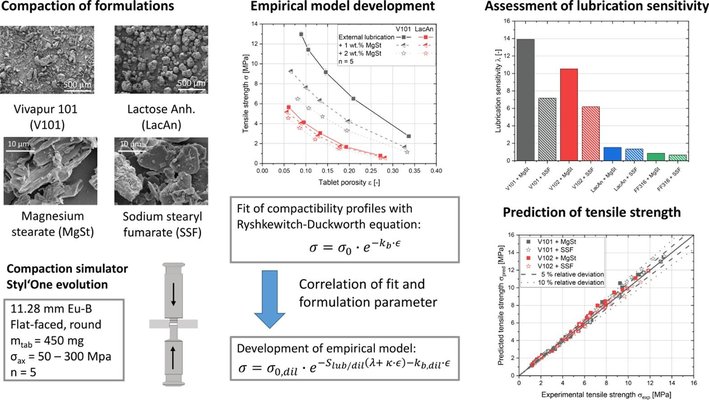
The tableting process for most pharmaceutical formulations necessitates the incorporation of lubricants to mitigate ejection forces, prevent tooling damage, and address tablet defects. However, the internal addition of lubricants is known to diminish the tensile strength of tablets, particularly those comprised mainly of materials that undergo plastic deformation. Presently, existing models exhibit limited quantitative predictive accuracy regarding the influence of lubricant concentration on the mechanical strength of tablets. This study seeks to address this gap by introducing a model based on the Ryshkewitch-Duckworth equation, capable of estimating the compactibility profiles of lubricated formulations.
Binary mixtures containing different diluents (microcrystalline cellulose and lactose) were prepared with common lubricants (magnesium stearate and sodium stearyl fumarate) and subsequently subjected to tableting. The resulting compactibility profiles were fitted using the Ryshkewitch-Duckworth equation, and the derived fit parameters (kb and σ0) were correlated with lubricant concentration. Subsequently, an empirical model was established that demands minimal experimental data and can predict the tensile strength of tablets containing lubricated diluents. As a result, this developed empirical model serves as an interesting and valuable addition to the existing array of multi-component compacting models. It provides an opportunity to expedite experimentation in the development of new tablet formulations.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment