Scientific papers
The primary route of drug administration is typically oral, with tablets being a widely utilized oral dosage form manufactured through powder compaction. Compaction plays a crucial role in determining the physical properties of tablets in drug product manufacturing, and extensive studies on powder compaction have addressed various issues such as capping, lamination, and sticking. These challenges become particularly apparent during scale-up from pilot to commercial production or when transferring production lines due to changes in rotary tablet presses.
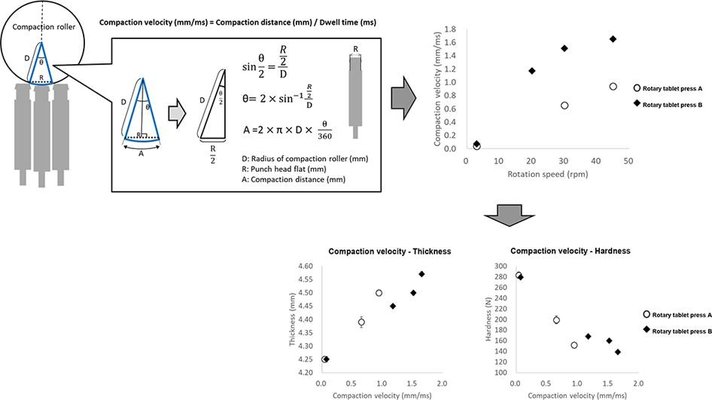
Differences in dimensions, including turret and compaction roller diameters and the angle between compaction rollers, among rotary tablet presses contribute to tabletting issues. The compaction cycle on a rotary tablet press involves filling, pre-compaction, main compaction, and ejection phases, and variations in the intervals between these phases exist across different presses. Additionally, force-time curves during compression exhibit three phases: consolidation, dwell, and decompression. The compaction simulator serves as a valuable tool for improving theoretical understanding of the compaction process, mimicking cycles of various rotary tablet presses, recording critical parameters, and aiding in stress-strain studies. It finds applications in pharmaceutical research and development, offering insights into compaction mechanisms, processing variables, scale-up parameters, troubleshooting during production, creating compaction databases, and characterizing new drugs or excipients.
The Stylone Evolution compaction simulator stands out for its ability to replicate the compaction cycle of actual rotary tablet presses based on dimensional information. It generates force-time and force-displacement curves, providing essential data such as compaction time, dwell time, ejection time, plastic energy, and elastic energy. These parameters facilitate quantitative evaluations of the compaction process. Numerous studies have utilized compaction simulators to assess tablet compaction processes, exploring factors like excipient compressibility, tableting properties, and the impact of punch velocity. However, there is a gap in studies that specifically evaluate compaction processes mirroring conditions of actual commercial rotary tablet presses.
This paper aims to quantitatively evaluate differences between various rotary tablet presses using the Stylone Evolution compaction simulator. Different rotary tablet presses exhibit mechanical variations leading to distinct compaction formations, influencing tablet properties even under identical compaction conditions. The compaction simulator enables the quantitative assessment of these differences, particularly focusing on compaction velocity during the dwell phase, where punch head flats directly contact compaction rollers. The study evaluates disparities in compaction velocity among rotary tablet presses under the same conditions and examines their effects on tablet properties and energy profiles during compaction.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment















