Scientific papers
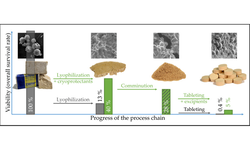
The preferred method for enhancing the stability and storage conditions of biopharmaceutical products is freeze-drying. Typically, these freeze-dried products are designed for administration via the parenteral route. However, many parenterally administered biopharmaceutical materials are employed to treat localized diseases, especially within the gastrointestinal tract. As a result, contemporary research is focused on developing alternative dosage forms for the oral delivery of biopharmaceutical molecules. Tablets, being the most widely utilized solid pharmaceutical dosage form for oral administration due to their numerous advantages, lack sufficient information regarding the possibility of compressing freeze-dried powders.
This study investigates the compaction behavior of freeze-dried trehalose powder, a commonly used cryoprotectant and lyoprotectant in the lyophilization of biopharmaceutical entities. The findings indicate that freeze-dried trehalose powder can be successfully tableted while maintaining its amorphous state. The resulting compacts exhibit distinctive properties, including compressibility, tabletability, brittleness, and viscoelasticity, in comparison to crystalline trehalose and classical pharmaceutical excipients.

Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment