Scientific papers
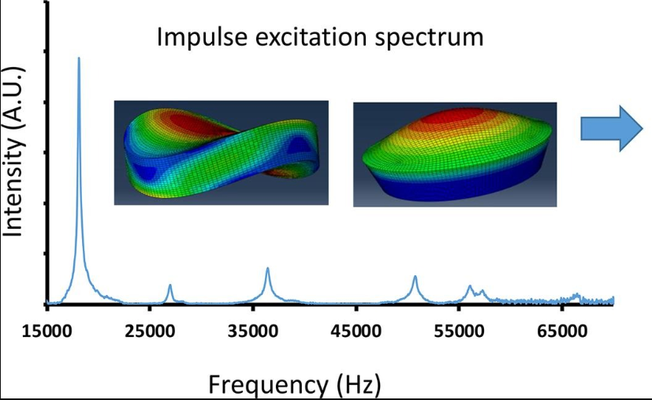
Elastic properties play a crucial role in tablet development, particularly in formulating the composition and defining process parameters. This article introduces impulse excitation as an innovative, rapid, and cost-effective technology for determining the elastic constants of pharmaceutical tablets. The method relies on detecting the natural resonance frequencies of solids. In the study conducted, tablets produced with various materials and compaction pressures revealed the clear identification of at least three resonance frequencies. Additionally, the shape of the resonance peaks in the spectrum provided insights into the viscoelastic nature of the tablet.
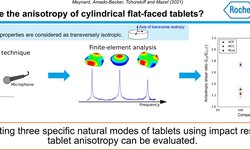
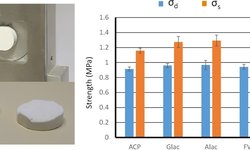
By utilizing the first two resonance frequencies and assuming isotropy, Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio for each tablet were calculated using the methodology outlined in ASTM E1876-01. As expected, the values obtained proved independent of tablet size and aligned with those reported in the literature using alternative methods. Furthermore, Finite Element Method (FEM) simulations indicated a correlation between the experimental value of the third resonance frequency and the numerically derived value, highlighting its connection to tablet anisotropy. Consequently, impulse excitation emerges as a promising methodology for investigating tablet anisotropy.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment