Scientific papers
Objectives:
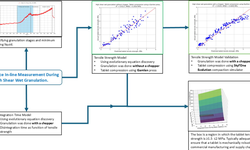
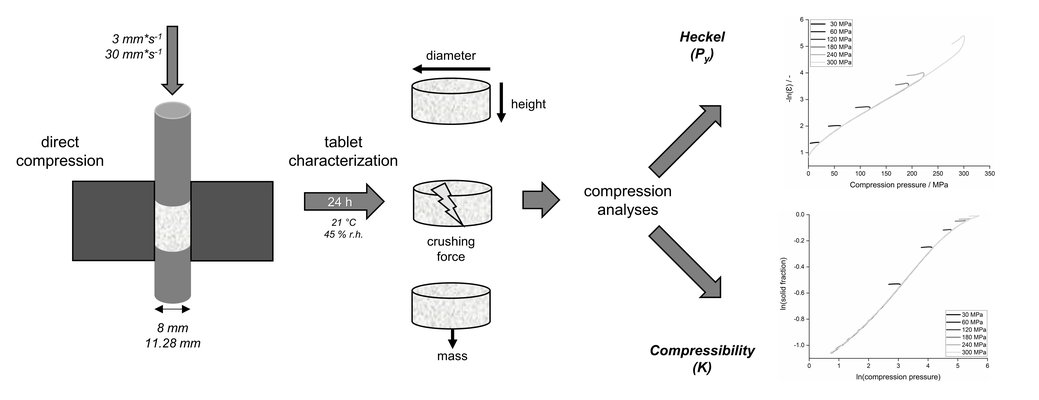
The compressibility of materials plays a crucial role in determining the tableting behavior and tablet properties throughout and after the manufacturing process. In this study, we explored the compressibility constant as an in-die method, comparing it with the Heckel analysis to describe material compressibility during tableting.
Methods:
We examined various parameters, including compression pressure, compression speed, and punch diameter, to assess the robustness of both methods and to gauge the informative value of compression parameters. Twelve common pharmaceutical excipients were utilized to encompass a broad range of material properties.
Key findings:
The compressibility constant was successfully employed as an in-die method, demonstrating greater robustness against influencing parameters during tableting compared to the Heckel analysis. While both methods exhibited a good correlation between out-of-die and in-die results, no correlation was observed between the compressibility constant and the yield pressure obtained from the Heckel analysis. Although both methods describe the volume reduction of materials under pressure, they focus on different material properties.
Conclusions:
In the realm of tableting material characterization, the compressibility constant can be an additional tool in the future, providing another compressibility parameter in conjunction with the yield pressure. This approach enhances our ability to comprehensively understand and describe the compressibility of materials during the tableting process.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment