Scientific papers
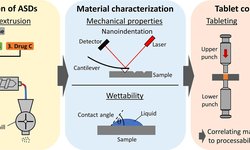
Hot-melt extruded sugar–starch pellets present an alternative to conventional sugar spheres, yet their coating properties require further investigation. The European Pharmacopoeia 8.6 and the United States Pharmacopeia 40 outline the composition of sugar–starch pellets without specifying manufacturing process requirements. Due to varied fabrication techniques, the physicochemical properties of pellets may vary. Consequently, this study explores the adhesion energies of three coating dispersions (sustained, enteric, and immediate release) on different pellet types. Surface energies of various corn starch types (normal, waxy, high-amylose) and sucrose pellets were analyzed using the sessile drop method, while the surface tensions of coating dispersions were examined using the pendant drop method. Adhesion forces were calculated based on these studies. Additionally, sugar spheres were characterized regarding particle size distribution, porosity, and specific surface area. Increasing sucrose content in pellets results in a more porous surface structure, enhancing their wetting behavior with coating dispersions. Adhesion energies of extruded sugar–starch pellets closely resemble those of commercial sugar spheres, meeting pharmacopeial requirements. Both pellet types are equally suitable for coating applications.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment