Scientific papers
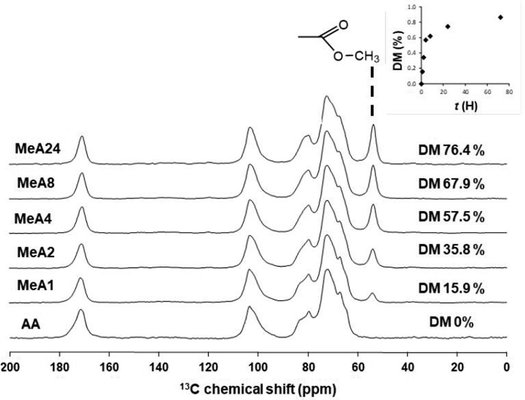
Evaluations have been conducted on methyl ester derivatives of alginic acid as potential multifunctional excipients for pharmaceutical direct compression. The utilization of alginic acid as an excipient in tablet formulation is constrained by certain drawbacks, including low tablet hardness and poor compressibility. The objective of this study is to enhance these properties through the esterification of alginic acid, a chemical modification commonly employed to improve the functionality of tableting excipients. It has been observed that the degree of methylation (DM) has a beneficial impact on the physico-chemical and mechanical properties of the resulting materials. Generally, an increase in the degree of methylation produced tablets with higher tensile strength and improved compressibility. Additionally, the modified alginates exhibited extended disintegration times compared to native alginic acid due to the introduced hydrophobicity. Finally, the functional versatility of the modified alginates was tested as disintegrating and filling/binding agents by formulating them with microcrystalline cellulose and lactose.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment