Scientific papers
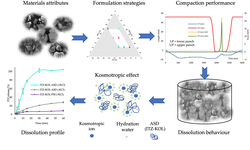
Amorphous solid dispersions (ASD) are increasingly utilized to enhance the oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble compounds. However, the hydrophilic polymers present in ASD often exhibit high water binding properties, leading to the formation of a gel on the tablet surface upon contact with water. This gel formation can significantly impact the rate and extent of drug release. In this investigation, the influence of inorganic salts on drug release from a tablet formulation incorporating an Itraconazole (ITZ) hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) extrudate was examined.
The cloud point of a 1% HPMC solution was determined, both with and without the presence of inorganic salts (KCl, KH2PO4, KHCO3, and KI), to categorize the salts based on their salting-out or salting-in effects. Kosmotropic effects on HPMC were noted for KCl, KH2PO4, and KHCO3, while KI exhibited a chaotropic effect. To validate the impact of these salts on drug release, tablets were prepared with 66% ITZ-HPMC extrudate (20:80 w/w%), 4% croscarmellose sodium, 30% microcrystalline cellulose, and varying types and amounts of KHCO3, KH2PO4, KCl, and KI (maintaining the same solid fraction of 0.83 – 0.85).
Tablets lacking salts exhibited slow release and low peak concentrations during dissolution in simulated gastric fluids. The addition of kosmotropic salts to the tablets increased the rate and extent of drug release, while the chaotropic anion iodide showed no effect. This effect was evident even with minimal amounts of inorganic salts (starting from 2%), and it tended to enhance with increasing salt quantity in the formulation. Tablets without salt displayed significant differences in dissolution profiles when stored under either dry or humid conditions, whereas tablets with kosmotropic salts showed minimal variation. In summary, this study mechanistically elucidated the impact of inorganic salts on ASD containing commonly used HPMC, providing valuable insights for developing robust formulations incorporating ASD.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment