Scientific papers
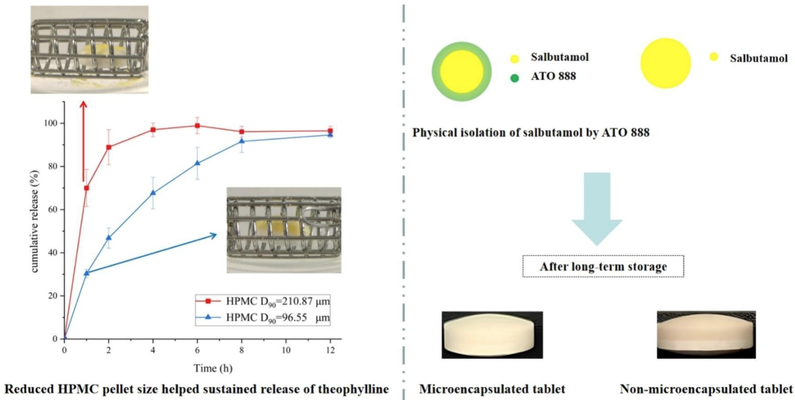
The Theophylline and Salbutamol Bilayer Sustained-release Tablets (Yi Xi Qing®), produced using wet granulation, are prone to discoloration during long-term storage, and the manufacturing process is less consistent and more laborious. In this study, a direct compression (DC) method was employed to develop equivalent and stable theophylline-salbutamol bilayer sustained-release (TBS) tablets, using Yi Xi Qing® as the reference formulation. The relative bioavailabilities of theophylline and salbutamol were 96.3% and 103.9%, respectively, with release similarity factors of 60.12 and 80.99. Salbutamol's stability during long-term storage was improved by lipid microencapsulation via hot-melt extrusion (HME), while using HPMC with a particle size smaller than 96.55 μm (D90) in the theophylline layer helped control theophylline release with minimal gel matrix material. These findings may provide valuable insights into the development of DC hydrophilic gel matrix bilayer tablets with high drug loading capacity.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment















