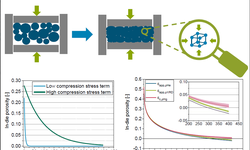
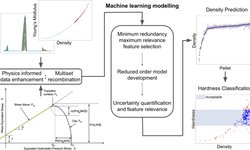
Scientific papers
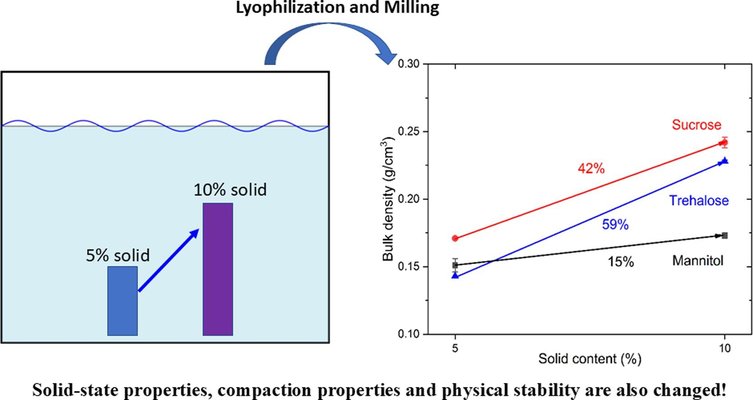
Interest in the oral delivery of biologics, often formulated via lyophilization, is growing rapidly. Lyophilization typically uses solutions with low solid content to optimize mass transfer and reduce drying time. However, this approach often produces lyophilized powders with low bulk density and poor flowability, complicating downstream processes essential for oral product development. While increasing the solid content in the initial solution could theoretically enhance the density of lyophilized cakes and powders post-milling, this strategy’s impact on powder density and flowability has not been experimentally validated. Additionally, the effect of higher solid content on other physicochemical properties of lyophilized materials remains unclear.
To bridge these knowledge gaps, we lyophilized three commonly used cryoprotectants at two solid content levels (5% and 10%) and systematically assessed their solid-state properties, bulk density, flowability, compaction behavior, and physical stability. Powders produced with higher solid content (10%) exhibited increased bulk density but still did not meet the requirements for seamless oral product development. Moreover, changes in solid content resulted in distinct solid-state properties, compaction characteristics, and stability profiles. These findings underscore the need for comprehensive characterization of lyophilized materials when modifying solid content during the development of oral solid dosage forms.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment