Scientific papers
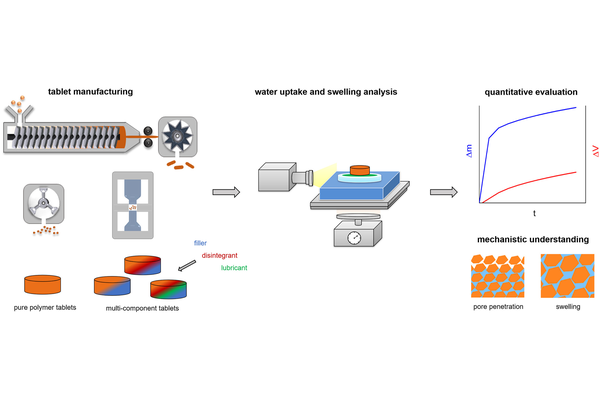
The functional characteristics of tablets are significantly shaped by the manufacturing process and the selection of excipients. Water uptake and swelling play crucial roles in tablet disintegration, dispersion, and subsequently, the dissolution of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). Tablets with high proportions of polymeric excipients, commonly used as carriers for APIs in amorphous solid dispersions (ASDs), may face challenges due to the formation of a gelling polymer network (GPN). This study conducts systematic investigations into the formulation development of tablets containing polymeric and other excipients, employing water uptake and swelling analysis. The study explores the impact of tablet composition, porosity, and the pH of the test medium. The pH was found to influence the analysis results for Eudragit L100–55 and Eudragit EPO. HPMC and Kollidon VA64 were observed to inhibit water uptake and swelling by forming a GPN. Tablets with high porosity, coarse particle size of the polymer, and the addition of fillers and disintegrants can mitigate the negative impact of a GPN on tablet performance. The application of lubricants was found to slow down the analyzed processes. The study further applies water uptake and swelling data to an empirical model, obtaining four characteristic parameters that facilitate a simple quantitative assessment of varying tablet formulations and structural properties.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment