Scientific papers
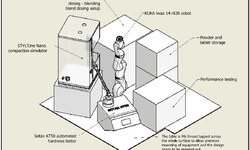
In this study, X-ray microtomography (XMT) was employed to investigate the microstructure of tablets. The objective was to obtain insights into their microstructure, facilitating a more profound interpretation of tablet properties such as mechanical strength and component distribution, leading to the development of qualified property functions. The study addresses challenges in image processing related to the accurate identification of solids and voids. Additionally, XMT measurements are critically compared with complementary physical methods for characterizing active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) content, porosity, and its distribution. These methods include mercury porosimetry, calculated tablet porosity, and Focused Ion Beam-Scanning Electron Microscopy (FIB-SEM).
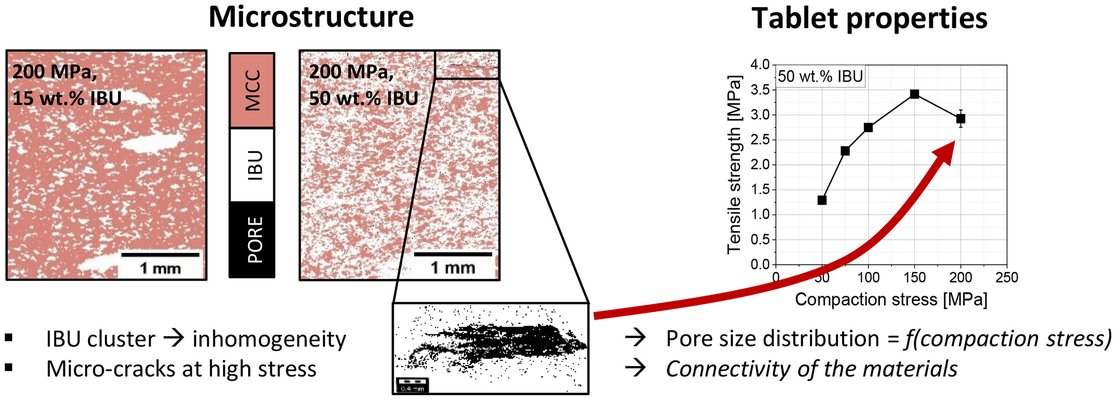
The porosity derived from XMT is generally lower than the calculated porosity based on geometrical data, attributed to the resolution of XMT in relation to pore sizes in tablets. As compaction stress and API concentration increase, deviations between the actual and calculated API decrease. XMT revealed the presence of API clusters in tablets containing >1 wt% of ibuprofen. The 3D orientation of components can be assessed by deriving cord lengths along all dimensions of the tablets. Increasing compaction stress results in higher cord lengths, indicating greater connectivity of the respective material. The lesser extent in the z-direction illustrates the anisotropy of the compaction process. Additionally, tablets without visible macroscopic damage exhibit cracks in the fabric. In conclusion, the application of XMT offers valuable structural insights, provided its limitations are considered and its strengths are enhanced by advanced pre- and post-processing techniques.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment