Scientific papers
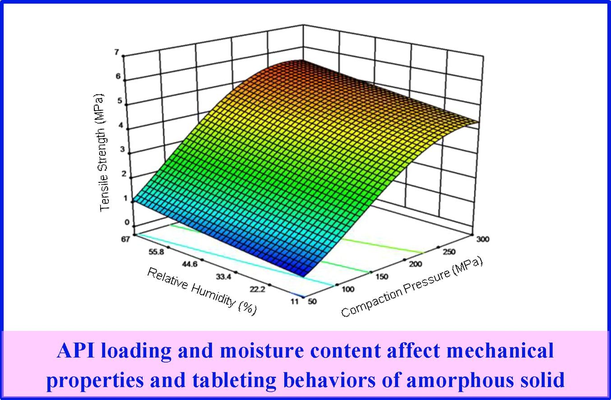
The mechanical characteristics of amorphous solid dispersions (ASDs) based on polymers are susceptible to alterations in relative humidity (RH) conditions. This study aims to elucidate the influence of RH on both the mechanical properties and tableting performance of Celecoxib-polyvinyl pyrrolidone vinyl acetate co-polymer (PVP/VA 64) ASDs. Utilizing the solvent evaporation technique, ASD films for nanoindentation were prepared and subsequently pulverized to obtain powder for compaction. The findings reveal a correlation between higher RH and lower Hardness (H) and Elastic Modulus (E). At a given RH, both E and H exhibit an increase with drug loading up to a maximum, followed by a decrease with further drug loading.
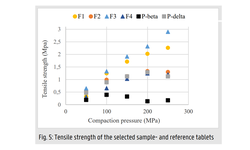
By employing ASD powders with a narrow particle size range (d50 = 9–14 µm), it was demonstrated that elevating RH from 11% to 67% results in enhanced tablet tensile strength for both pure PVP/VA 64 and the ASDs. However, the magnitude of the increase in tablet tensile strength depends on their mechanical properties (H and E) and drug loading. At higher compaction pressure and increased RH, the impact of ASD mechanical properties on tabletability diminishes because the particles are nearly fully deformed, resulting in approximately the same bonding areas. Consequently, the difference in tablet strength is predominantly influenced by inter-particulate forces of attraction. This understanding of the key processing conditions, namely RH and compaction pressure, will inform the design of a robustly manufacturable ASD tablet formulation.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment