Scientific papers
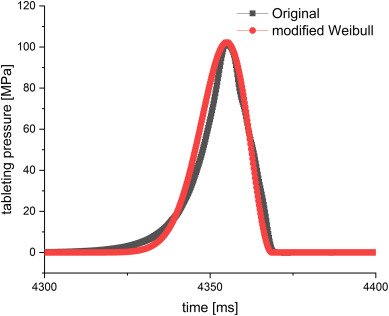
Mini-tablets, increasingly attractive in the pharmaceutical industry for their clinical and biopharmaceutical advantages, lack a comprehensive investigation of technological aspects. This study delves into the impact of punch size and tableting pressure using industrially relevant excipients such as microcrystalline cellulose, lactose, isomalt, and Ludiflash®. The investigation employs 8 and 11.28 mm punches for conventionally sized tablets and 1, 2, and 3 mm punches for mini-tablets. To assess the effect of tablet size on deformation behavior and mechanical properties, compressibility, compactibility, and tabletability plots are generated and analyzed. Deformation behavior is scrutinized through In-Die Heckel plots and a modified Weibull function. Additionally, specific plastic energy (SPE) profiles are derived from force-displacement plots. The study analyzes the impact of adjusting the aspect ratio to 1, as in conventionally sized tablets, on deformation behavior and tabletability.
The effect of tablet size on deformation behavior primarily reveals lower yield pressures for conventionally sized tablets, while comparable SPEs are observed across all tablet sizes. Furthermore, mini-tablets exhibit enhanced compactibility, with higher tensile strengths achieved at lower solid fractions, contingent on the excipient. However, no superior tabletability properties are observed for mini-tablets compared to conventionally sized tablets.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment